Do you know how difficult woodpecker lips are to break? These extraordinary birds are known for their rhythmic drumming on trees, but they also have an unusual trait that distinguishes them from other birds. In this exploration, we will look into the fascinating question of how hard is the woodpecker’s lips, and discover the secrets behind this remarkable feature of woodpecker biology.
The hardness of woodpecker lips is a testament to nature’s engineering talent. A protective shield is provided by these lips during drilling, and the woodpecker uses them to feed. As you learn about how woodpecker lips are composed and how their evolutionary adaptation is influenced by their uniquely structured lips, you will gain insight into the fascinating world of these birds and the survival advantages they provide.
As you embark on this journey, be prepared for revelations about the anatomy, feeding habits, and evolutionary history of woodpeckers. The keratinized outer layer of their lips, as well as intricate communication through drumming patterns, all contribute to the woodpecker’s ability to perform at such a high level. The mystery of woodpecker lips will be explored, and we will gain a deeper appreciation for how resilient these feathered wonders are.
Woodpecker Anatomy
In the intricate tapestry of nature, the woodpecker emerges as a marvel, captivating enthusiasts and researchers alike with its unique anatomy. As we delve into Section 1: Woodpecker Anatomy, a comprehensive understanding of these avian wonders unfolds, shedding light on the physical characteristics that set woodpeckers apart in the avian kingdom.
Overview of Woodpecker Physical Characteristics:
Woodpeckers, characterized by their vibrant plumage and distinctive markings, boast a compact yet powerful physique. Their bodies are streamlined for efficiency in flight, with strong wings and a sturdy tail providing stability. Remarkably, their zygodactyl feet, equipped with two toes forward and two backward, enable a secure grip on vertical surfaces – a crucial adaptation for their arboreal lifestyle.
Beak Structure and Adaptations for Drilling:
Central to the woodpecker’s prowess is its beak – a masterful tool honed by evolution for precision and resilience. The beak’s chisel-like structure facilitates efficient drilling into wood, while its robust composition withstands the repeated impacts of pecking. This adaptation is not merely for feeding but also serves as a means of communication and establishing territory, underscoring the multifaceted role of the woodpecker’s beak in its daily life.
The Role of the Tongue and Hyoid Bone:
Delving deeper into woodpecker anatomy, the tongue emerges as a fascinating component in their feeding strategy. Unlike most birds, woodpeckers possess an extended, barbed tongue, which acts as a versatile tool for extracting insects from crevices. Complementing this, the hyoid bone – a structure unique to woodpeckers – acts as a shock absorber during the relentless pecking. This intricate interplay of tongue and bone showcases nature’s ingenuity, allowing woodpeckers to exploit niches that other birds might find challenging.
In the grand scheme of evolution, woodpeckers stand as exemplars of specialized adaptation, each aspect of their anatomy finely tuned for survival in their chosen habitats. The interplay between physical characteristics, beak structure, and the specialized adaptations of the tongue and hyoid bone paints a portrait of efficiency and resilience. Beyond the allure of vibrant plumage and rhythmic drumming, it is this precise orchestration of anatomical elements that defines the woodpecker’s place in the intricate web of biodiversity.
As we peer into the intricate details of woodpecker anatomy, it becomes evident that every facet serves a purpose – a testament to the evolutionary forces that have shaped these birds over millennia. This exploration not only enriches our understanding of woodpeckers but also highlights the delicate balance of nature’s design, where form seamlessly aligns with function in the ongoing dance of survival.
Woodpecker Feeding Behavior
In the vibrant tapestry of nature, the feeding behavior of woodpeckers emerges as a captivating dance, finely tuned to the rhythms of survival. As we navigate Section 2: Woodpecker Feeding Behavior, an intricate exploration awaits, unraveling the nuances of these avian foragers and the significance of their feeding strategies.
Exploration of Woodpecker Feeding Habits:
Woodpeckers, the rhythmic percussionists of the avian world, exhibit a diverse array of feeding habits that reflect their adaptability and resourcefulness. From probing the bark of trees to scouring the crevices of branches, these birds employ a repertoire of techniques to extract sustenance. The exploration of woodpecker feeding habits reveals a keen reliance on insects, larvae, and spiders, forming the cornerstone of their diet. This dietary preference not only sustains woodpecker populations but also serves as a crucial ecological balance, controlling insect populations in their habitats.
Types of Trees and Surfaces They Target:
In the pursuit of sustenance, woodpeckers display a remarkable selectivity in the types of trees and surfaces they target. Deciduous and coniferous trees alike bear witness to the probing beaks of these avian foragers. The choice of trees often aligns with the presence of wood-boring insects, a delicacy for woodpeckers. The rhythmic tapping on tree trunks is not just a percussion performance; it is a strategic exploration, a quest for hidden treasures beneath the bark. This selective targeting showcases the woodpecker’s ability to adapt its feeding behavior to the unique characteristics of its chosen habitat.
Explanation of the Drilling Process and Its Significance:
Central to the woodpecker’s feeding behavior is the mesmerizing drilling process, an artistry of motion and precision. The woodpecker’s beak, acting as a formidable chisel, punctuates the silence of the woods with rhythmic strikes. Each tap is a calculated move, resonating with purpose. The drilling is not merely a means of extracting food; it serves a dual purpose – communication and territory establishment. The resonant drumming signals both presence and prowess, a language understood by other woodpeckers in the vicinity. This drilling-induced percussion holds significance in the intricate social fabric of woodpecker communities, defining territories and attracting potential mates.
As we peel back the layers of woodpecker feeding behavior, a tapestry of ecological interdependence and survival strategies unfolds. The exploration of their diverse habits, selective targeting of trees, and the rhythmic drilling process reveals a nuanced dance between instinct and adaptation. In the grand symphony of nature, woodpeckers play a pivotal role, not just as foragers but as architects of their ecological niches. As we witness the rhythmic percussion echoing through the woods, we glimpse into the dynamic world of woodpecker feeding behavior – a symphony of survival etched into the heart of the natural order.
Woodpecker Lip Composition

In the intricate world of woodpecker anatomy, Section 3 unveils a compelling exploration of Woodpecker Lip Composition, offering a nuanced understanding of the structural marvels that define these avian wonders.
Examination of the Structure and Composition of Woodpecker Lips:
Woodpecker lips, often overshadowed by the rhythmic drumming and vibrant plumage, harbor a complex architecture designed for resilience and functionality. The examination of their structure reveals a threefold composition that sets them apart in the avian kingdom:
Epidermis and Dermis:
- The outer layer, composed of a specialized epidermis and dermis, forms the primary barrier against external forces.
- Rich in keratin, this layer provides a robust shield, shielding the lips from abrasions and impacts during the woodpecker’s relentless pecking.
Muscle and Connective Tissue:
- Beneath the protective outer layer lies a network of muscles and connective tissue, adding a layer of flexibility to the woodpecker’s lips.
- This intricate balance of rigidity and pliability enables the lips to withstand the intense forces generated during drilling while maintaining agility for precise movements.
Vascular Network:
- A complex vascular network ensures efficient blood supply to the lips, contributing to rapid recovery from any minor injuries sustained during pecking.
- This adaptive vascularization aids in preventing bruising and facilitates the swift healing required for the woodpecker’s high-impact feeding behavior.
Insights into the Keratinized Outer Layer:
The keratinized outer layer of woodpecker lips emerges as a pivotal element in their composition, embodying the essence of durability and impact resistance. This keratinized sheath acts as a natural armor, providing the lips with a tough, resilient exterior. As we delve into the specifics:
Stratified Keratinocytes:
- The outermost layer comprises stratified keratinocytes – densely packed cells with a high keratin content.
- This arrangement forms a formidable barrier that shields the lips from the wear and tear associated with constant pecking.
Microscopic Architecture:
- Microscopic examination reveals a lattice-like structure within the keratinized layer, distributing and dissipating impact forces evenly.
- This intricate architecture not only enhances durability but also minimizes the risk of injuries sustained during the woodpecker’s feeding activities.
Discussion on How the Lips Absorb and Distribute Impact Forces:
The woodpecker’s feeding behavior, characterized by rapid and forceful pecking, necessitates a mechanism for absorbing and distributing impact forces. The lips, equipped with their unique composition, excel in this regard:
Impact Absorption:
- The keratinized outer layer acts as a shock absorber, cushioning the impact forces generated during each peck.
- This absorption mechanism is vital for preventing injuries to the delicate structures beneath the lips, ensuring the woodpecker’s feeding efficiency remains unhindered.
Force Distribution:
- The distribution of forces across the lips is orchestrated by the interplay of muscles and connective tissue.
- This orchestrated distribution prevents localized stress points, contributing to the overall resilience and longevity of the woodpecker’s lips.
In unraveling the intricacies of Woodpecker Lip Composition, we uncover a tale of adaptability and evolutionary mastery. From the keratinized outer layer’s role as a resilient shield to the strategic absorption and distribution of impact forces, woodpecker lips stand as a testament to the harmonious marriage of form and function in the natural world.
Woodpecker Lip Hardness
In the realm of woodpeckers, Section 4 unfurls a captivating exploration of Woodpecker Lip Hardness, delving into the scientific inquiries that dissect the resilient nature of these avian lips and the profound implications for their feeding habits and survival.
Analysis of Studies Measuring Woodpecker Lip Hardness:
Embarking on an intellectual journey, researchers have meticulously probed the hardness of woodpecker lips, employing advanced techniques to unravel the secrets held within. The analysis of studies unfolds a narrative of biological ingenuity:
Hardness Metrics:
- Studies employ sophisticated metrics, such as Vickers hardness tests, to quantify the hardness of woodpecker lips.
- Results showcase an exceptional level of hardness, surpassing expectations and challenging conventional wisdom regarding the softness of avian tissues.
Material Composition:
- Spectroscopic analysis delves into the material composition of woodpecker lips, uncovering the prevalence of keratin and collagen.
- This unique composition contributes to the hardness and durability of the lips, providing insights into the specialized adaptation that enables the woodpecker’s relentless pecking.
Comparison with Other Bird Species:
In the avian landscape, woodpeckers emerge as outliers in terms of lip hardness, challenging preconceived notions about the malleability of bird tissues. A comparative analysis with other bird species sheds light on the exceptional nature of woodpecker adaptations:
Avian Diversity:
- Woodpeckers stand apart from the avian spectrum, exhibiting a lip hardness unparalleled among their feathered counterparts.
- Comparative studies with non-woodpecker species highlight the distinct evolutionary trajectory that has led to the development of these remarkably resilient lips.
Adaptation to Feeding Strategies:
- The comparison underscores how lip hardness aligns with the woodpecker’s unique feeding strategies, distinguishing them in the ecological niche they occupy.
- While other birds may rely on different mechanisms for feeding, woodpeckers have evolved with an emphasis on durability to withstand the intense forces of pecking.
Implications of Hard Lips for Feeding and Survival:
The exceptional hardness of woodpecker lips extends beyond a mere anatomical curiosity; it carries profound implications for their feeding efficiency and overall survival in diverse habitats:
Feeding Efficiency:
- The hardness of woodpecker lips facilitates efficient drilling into wood, enabling the extraction of insects residing deep within tree bark.
- This feeding efficiency provides woodpeckers with a competitive advantage, ensuring a reliable food source and contributing to their ecological role in pest control.
Survival in Natural Habitats:
- In their natural habitats, where woodpeckers engage in territorial disputes and vie for resources, hard lips play a crucial role.
- The ability to withstand repeated impacts ensures the woodpecker’s survival in competitive environments, where feeding, communication, and territorial assertion are intertwined.
As we unravel the layers of Woodpecker Lip Hardness, the confluence of scientific inquiry and natural adaptation becomes apparent. Beyond the intricacies of hardness metrics and material composition, woodpecker lips emerge as a testament to the evolutionary marvels that equip these birds for success in their dynamic ecosystems. This exploration not only enhances our understanding of woodpecker biology but also underscores the intricate balance between form and function in the tapestry of the natural world.
Evolutionary Adaptations
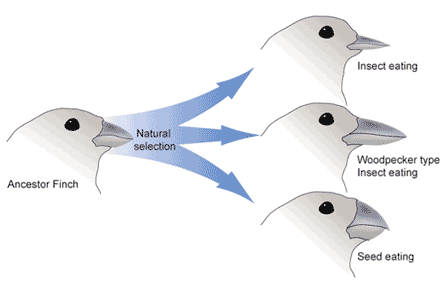
In the intricate dance of evolution, Section 5 delves into the fascinating narrative of Woodpecker Evolutionary Adaptations, unraveling the nuances of how these avian marvels have sculpted their anatomy over time to exhibit the resilience embodied in their hard lips.
Overview of the Evolutionary Aspects of Woodpecker Anatomy:
Woodpeckers, nestled within the rich tapestry of avian diversity, epitomize the artistry of evolutionary adaptations. As we embark on an overview of their anatomy, a panoramic view emerges, showcasing the remarkable features that define woodpeckers in the grand theater of evolution:
Specialized Beak Structure:
- The evolution of a specialized beak structure, characterized by a robust and chisel-like form, reflects the woodpecker’s adaptation to its feeding behavior.
- Over time, this evolution has sculpted a beak that serves as both a tool for drilling into wood and a communication apparatus through rhythmic drumming.
Hyoid Bone Modifications:
- The evolutionary modifications in the hyoid bone, unique to woodpeckers, act as a shock absorber during the relentless pecking.
- This adaptation showcases the fine-tuning of anatomical structures to accommodate the intense forces generated during feeding, marking a distinctive feature in their evolutionary journey.
Examination of How Woodpeckers Developed Hard Lips Over Time:
The journey of woodpeckers toward the development of hard lips unfolds as a testament to the selective pressures and adaptive forces that have shaped their evolutionary trajectory. An examination of this journey reveals key milestones:
Selective Pressures for Feeding Efficiency:
- Through the ages, the relentless pursuit of insects hidden within trees has exerted selective pressures favoring enhanced feeding efficiency.
- Woodpeckers, in response to these pressures, have evolved lips with a keratinized outer layer – a protective shield that facilitates efficient drilling and minimizes wear and tear.
Iterative Refinements:
- The iterative nature of evolution is evident in the gradual refinements of lip hardness over successive generations.
- Woodpeckers, honing their adaptations through natural selection, have arrived at a delicate balance of hardness and flexibility, optimizing their ability to sustain the impacts of pecking.
Insights into the Survival Advantages Provided by Hard Lips:
The evolution of hard lips in woodpeckers is not merely a cosmetic alteration but a strategic adaptation that confers notable survival advantages. Insights into these advantages shed light on the ecological niche they occupy:
Enhanced Feeding Success:
- The hard lips of woodpeckers translate into enhanced feeding success, as they can effectively access insect larvae deeply embedded within tree bark.
- This advantage contributes to their ecological role as pest controllers, impacting insect populations in their habitats.
Competitive Edge in Territorial Dynamics:
- In habitats where woodpeckers engage in territorial disputes, the survival advantages of hard lips become apparent.
- The ability to assert dominance through efficient feeding and communication reinforces their competitive edge in the intricate dance of territorial dynamics.
In the grand symphony of evolution, woodpeckers have orchestrated a masterpiece of adaptation, sculpting their anatomy to meet the demands of their ecological niche. From specialized beak structures to iterative refinements and the strategic development of hard lips, each facet of their evolutionary journey paints a portrait of resilience and efficiency. As we delve into the intricate details of Woodpecker Evolutionary Adaptations, we witness the ceaseless march of life, honed by the forces that have shaped the avian wonders we marvel at today.
Woodpecker Communication
In the vibrant realm of woodpecker behavior, Section 6 unveils the captivating symphony of Woodpecker Communication, where beaks transform into instruments and rhythmic drumming becomes a language that resonates through the wooded landscapes.
Brief Exploration of How Woodpeckers Use Their Beaks for Communication:
Woodpeckers, renowned for their rhythmic drumming, ingeniously repurpose their beaks as communication tools, creating a unique form of avian dialogue. This brief exploration sheds light on the multifaceted ways in which woodpeckers utilize their beaks for communication:
Beak Percussion:
- Woodpeckers leverage their specialized beak structure to engage in percussive drumming on various surfaces, ranging from tree trunks to metal structures.
- The resonant beats serve as a means of communication, conveying messages related to territory, mating, and warning signals.
Rhythmic Patterns:
- The rhythmic patterns produced by woodpeckers are not arbitrary; they carry distinct meanings within the avian community.
- Different drumming patterns may signal aggression, establish territorial boundaries, or serve as an acoustic beacon to attract potential mates.
Visual and Auditory Cues:
- Beyond the auditory aspect, woodpecker communication often involves visual cues, as individuals may observe the drumming displays of their counterparts.
- This integration of visual and auditory signals enhances the efficacy of communication in their wooded habitats.
Discussion on Drumming Patterns and Signals:
Delving deeper into the intricate language of woodpecker drumming, we unravel the nuanced discussion on the diverse patterns and signals embedded within this rhythmic communication:
Territorial Drumming:
- Woodpeckers employ distinct drumming patterns to assert territorial dominance, creating a sonic perimeter that warns off potential intruders.
- The intensity and frequency of the drumming signal the strength and vigor of the woodpecker, influencing the dynamics of territorial disputes.
Mate Attraction and Courtship:
- The resonant beats of woodpecker drumming extend beyond territorial claims to play a pivotal role in mate attraction and courtship rituals.
- Males may engage in elaborate drumming displays to showcase their vitality and attract potential mates, with the drumming acting as a charismatic performance in the avian dating scene.
Alarm Calls and Warning Signals:
- Woodpeckers also utilize drumming as an alarm call, signaling potential threats or dangers to the community.
- The rapid and erratic drumming patterns in response to perceived threats serve as warning signals, prompting other woodpeckers to adopt vigilant postures.
As we immerse ourselves in the rich tapestry of Woodpecker Communication, the beak becomes more than a tool for feeding; it transforms into a communicator’s wand, orchestrating a symphony of signals that echo through the forest. The rhythmic drumming patterns, laden with meaning, reveal the depth of social dynamics and survival strategies ingrained in woodpecker behavior. In the intricate language of percussive communication, woodpeckers carve out a unique niche, where the forest resounds not just with the sounds of nature but with the deliberate beats of avian conversation.
Key points
Following our examination of the fascinating intricacies of woodpecker lips, we have now revealed their intricate features. We followed the fascinating world of woodpecker anatomy, feeding behavior, and evolutionary adaptations as a result of the question we were most curious about: How hard are woodpecker lips?
The keratinized outer layer of woodpecker lips serves as a testament to the technological innovation of nature. As we looked at the hardness of these lips, it became clear that they play an important role in the woodpecker’s ability to withstand impact forces during drilling. This resilience helps to feed the bird not only in its natural habitat, but also to supplement its food intake.
As a result of their evolutionary studies, it became clear that the gradual development of hard woodpecker lips was a result of their adaptation. We gained another layer of insight into the significance of woodpeckers’ distinctive features as a result of the drumming patterns we used.
As we finish our journey, consider the woodpecker, a creature whose lips complement form and function like nothing else on earth. The woodpecker’s lips stand as a testament to evolution’s most amazing feats, from the rhythmic drumming heard in forests to the silent battles fought during feeding. Our quest to unravel the mystery of woodpecker lips has provided us with answers and sparked a deeper appreciation for the wonders hidden within the seemingly simple act of pecking on wood.
Amhil Khan, a dedicated nature enthusiast and the founder of BirdsOfTheWild.com, is a passionate advocate for the captivating world of avian wonders. With a deep-seated curiosity about the intricate lives of birds, Amhil’s journey began as a fascination and has evolved into a mission to inspire others to appreciate and protect these magnificent creatures.
Amhil’s love for birds led to the creation of Birds of the Wild, a platform where his expertise in ornithology, coupled with his captivating storytelling, provides readers with an immersive and educational experience. Through his lens and words, he captures the essence of birds in their natural habitats, offering a glimpse into their behaviors, migrations, and the ecosystems they inhabit.

